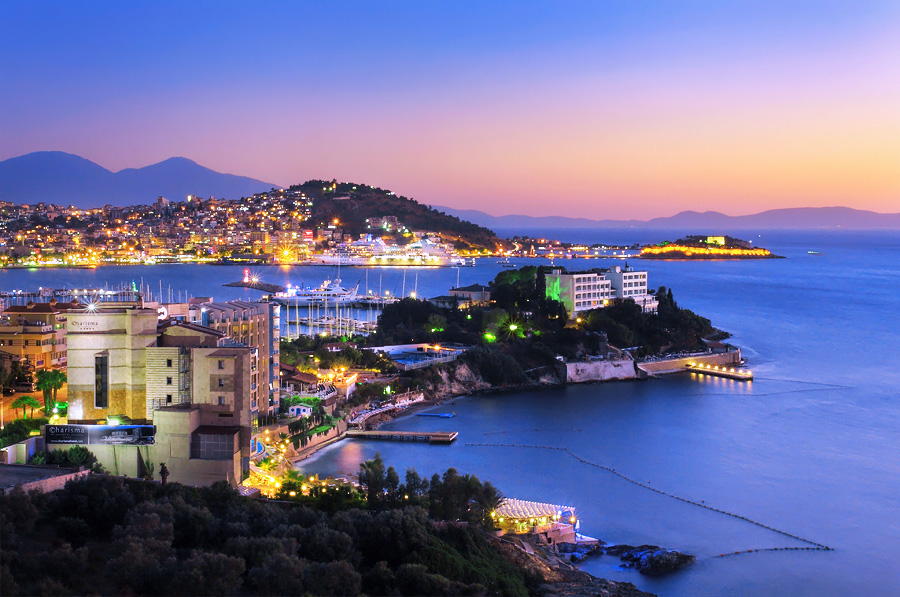
Kusadasi
Kuşadası History
Kuşadası is a county of Turkey’s Aydın province. The county located in the north west of the province is 71 km from Aydın city center and 95 km from İzmir city center. Away. The district, which is located on the Aegean Sea coast, is a major tourism center of Turkey.
The area of the county is 264 km2 and according to the results of the 2009 Population Census based on Yearly Adrese, 81 295 people live
Near Kuşadası, it is believed that it was founded by Ionlar with the name of Neopolis connected to Ephesus in the place called Yilancu Burnu.
The city was established before, on the outskirts of Pilavtepe, at the place called Andızkulesi. After a while the Venetian and Genoese who belonged to the Byzantines were dominant in economic terms. Kuşadası with the reasons of transportation difficulties; It was taken from Andızkulesi mevkii and it was established with the name of Scarpa Nuova in present place.
Kuşadası Bay and its immediate surroundings, which Kuşadası gave its name, are known as centers of art and culture and have hosted many different civilizations since the early ages.
B.C. In 3000 BC, Aioller in the 11th century, BC In the 9th century, the Ions dominated the region. The area between Büyük Menderes and Gediz Rivers takes the name of Ionia in antiquity. Ions, merchants and sailors, soon became rich through overseas trade and gained a superior political power. In the history they established 12 cities named “Ion Colonies”.
Kuşadası was one of the main ports of Anatolia that opened to the Mediterranean in antiquity. It was called Neopolis by that time. B.C. In the 7th century, the Lydians, whose capitals were Sardes, dominated the region.
B.C. The Persian domination that started in 546 BC It continues until Alexander the Great seized all of Anatolia in 334. After that, a new era, a new kind of art and culture understanding becomes dominant as a synthesis of Greek civilization and indigenous Anatolian civilization in Anatolia and this age is called “Hellenistic Age”. Ephesus, Milet, Priene and Didim are the most famous cities of this devrin.
B.C. In the 2nd century, the Romans dominated the region. In the early years of Christianity, St.Jean from Mother Mary and his disciples came to Ephesus and became a religious center. Miletus is also the episcopal center in the Christian era. It is known in the Byzantine Period as “Ania”. Kuşadası is a harbor used by pirates in the middle ages. In the 15th century, the Venetians and Genoese took the name of the city “Scala Nuova”.
In 1086, the territory of the first Suleyman Shah begins to dominate the Seljuk State. The region has become an export gate to the Aegean region of the caravan routes in this period. However, the sovereignty of the Seljuk State took a short time due to the 1st Crusades and again passed into the hands of Byzantium. At the end of the 1280s the Menteşeoğulları entered the Ottoman domination between 1397-1402. Although the Ottomans passed the turn of the Aydınoğulları between 1402 and 1425, the Ottomans certainly seized the region.
Kuşadası, in 1413, 1.Mehmet (Çelebi) joined the Ottoman domination. After this date, the city was completely in the hands of the Turks and began to fill with the works of the Turks. These walls were built by Mehmet Pasha, which caravans today’s Caravanserai and Kuşadası.
The city surrounded by walls was only able to enter from three doors. One of these doors separates Barbaros Hayrettin Paşa Street and Kahramanlar Cad, and the upper part is used today as the City Traffic Regions Authority. Other gates are not available today.
Güvercinada, who served as an important military base for the Byzantines in Küçükada, saw a major renovation in 1834 and built a famous castle. The name “Kuşadası” comes from this town.
Kuşadası entered the occupation of Greece during the War of Independence between 1919-1921, with the withdrawal of Italy, and escaped the enemy invasion on 7 September 1922.
PYGELA
It was an ancient settlement built on the hill where the Disco of today’s Clup Pigale and Kühfete Holiday Village and A’la Carte Restaurant. The world is Pygela, the first city to be established as a health city. Agamemnon, the king of Argos, built the cities of Pigale in Kuşadası and Pigale in Izmir and Agamemnon in Izrnir to restore tired soldiers and repair war vessels during the 10-year Trojan wars.
Both cities succeeded in bringing back the troubled health of their soldiers and their weary morale with the healing waters nearby. The pond – marsh behind the Pine Harbor and Tusan Hotel where the present Pine Bay Resort is located was the Port of Pigale and ship maintenance places. Pigale Health Town and Port became a place of recreation for the soldiers of Alexander the Great who later came to Ephesus.
ANAIA – ANEA (SOĞUCAK) – WOMEN’S QUALITY
This seaside town in the Carta region, which falls in the face of the Isis Island, served as a shelter for pirate ships as well as a commercial center as well as a harbor-friendly harbor. Anaia was in possession of those who were exiled from Samos, the patron of Athens during the Athenian-Spartan battles (M.9 431-404), those who escaped, those who were hostile to the administration there. Here, both the Samos leaders and the Athenians were serving the Spartans. The city is called Thukydides because of the events of this period. In 1304, the Necropolis near Anea and its present Kadi Castle was under the rule of the Byzantines at that time, hosting a Genoese colony. The Genoese living in the city of Anea, after the Kemalpaşa (Nif) settlement, organized anti-piracy attacks against the Venetian merchant ships with the local Greeks. After Ania, Ephesus and İzmir, he passed to Turkish rule in 1317.
PANIONION
It was the “Karyon – Auto Tepe” in Kale Tepe, which is located within the borders of the National Park in the Dilek Peninsula, located in Guzelcamli District, the center of the semi-religious, semi-political Paionion Union formed by the city of Ion. Auto Hill is a sacred place that one site brings to the waterfall. B.C. In 700, the delegates of the 12 city states gathered in Panionion on certain days of the year and made important political decisions. Helikonios, on behalf of the sea god Poseidon, who is called by the side name, discussed the problems of the cities with the famous sacrificial ceremonies made by the lonia troops in this sacred area and made a recommendation to one of the city states and made joint decisions on important issues. Panionion was also well known as a center of prophecy. In order to be prostituted, the lungs of the sacrificial animals had to be presented to God as whole.
NEAPOLIS
It is the second settlement in the south of Güvercin Island, which is one of the first settlements of Kuşadası founded by the Ions in ancient times. There is still an ancient city under the sea.
ILICA HILL
Ilıca, the place where Aka are settled in the years when they migrated to Western Anatolia for the first time, is evidence of the fact that Kuşadası is a city that lived 3000 years ago. The walls made of large stone have survived to this day.
GÜVERCİNADA
It is a small island on the coast of Kuşadası. It is connected to the land by a breakwater, there is a castle built during the Byzantine period. He served as an outpost against the attacks from other islands during the Ottoman Empire and especially during the Mora rebellion. It is also known as “Pirate Castle” among the people because it uses against pirates. The castle was restored, illuminated and presented to the service of tourism.
ÖKÜZ MEHMED PASHA CARAVANSARAYI (KURŞUNLU HANI)
The caravanserai was built by Öküz Mehmed Paşa in 1618 for a maritime trade and is a two-storey, courtyard building. (According to some reports, it is said that the Governor of Aydin, Öküz Mehmed Pasha, did not make the fortress and repaired it in the year of 1607. The bastion and pothole holes in the Kursunlu Han show that the fortress is exposed to violent battlements, around 28.50 Meters x 21.60 meters The presence of this Caravansaray indicates that one of the caravan routes of Kuşadası at the time of the Ottomans was the export port of commercial goods sent from the inner parts of the country at the end of the Ottoman period.The structure is explained in detail in Evliya Çelebi’s ” Was rented and restored by “Clup Mediterranee” in 1966 and opened as “Turistik” Accommodation Management.
MORE