Aydin City Museums,
Aydin Museum: In 1950 works were first collected from the region of Aydin, in particular from the ruins of the ancient city of Tralles which was the first settlement of Aydin. They were gathered in the garden of Aydin Men’s Art Institute, and in 1959 moved to a room and the garden of Zafer primary school. When the need for a new museum building was felt in 1968, construction of a new building began, and in 1973 when the building was completed, Aydin Museum was opened to the public. At the time of the opening, the museum contained 1488 archaeological, and 2030 ethnographic works, and 1236 coins. Aydin Museum is divided into two sections – archaeological and ethnographic.
You can check Ephesus tours on our website.
In the archaeological section the following objects are exhibited:
1 — Prehistoric dishes, tools made from flint and obsidian, polished stones, idols, arrowheads, stone axes, coins from the Greek, Roman and Byzantine periods, marble heads of men and women, and has reliefs.
2 — Findings from the Hellenistic and Roman periods, figurines. lamps, glass objects, vases, gold crowns and diadems, busts and ceramics from the Hittite period.
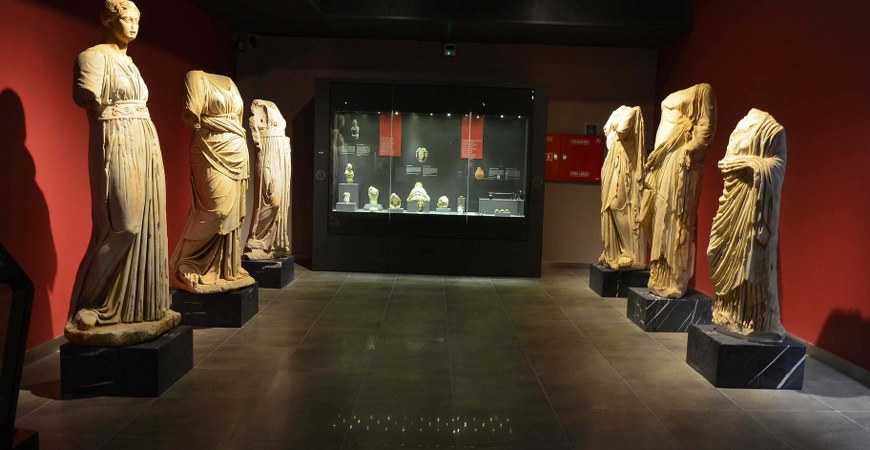
3 — In the gallery of marble works are displayed bas-reliefs, a bust of the Goddess Athene, a statue of Nike, a bust of Aurelius, torsos, marble figurines, and building stones. In the ethnographic section of the museum are exhibited embroidery, napkins, bed covers, women’s and tribal costumes, silver ornaments. and examples of knitting and weaving from the region of Aydin. In the garden are building stones and statues from the Roman period, sarcophagi, grave steles, inscriptions.
Aphrodisias Museum
After years of archaeological excavations of the ruins of the ancient city of Aphrodisias, which is situated in the village of Geyre in the sub-province of Karasu in Aydin, the theater, Temple of Aphrodite, Odeon, Stadium, Agora, and baths have been to a large extent restored. Objects uncovered by excavations, particularly sculpture, in Aphrodisias, which was the site of important settlements from the Bronze Age (2800 – 2200 BC) to the Byzantine period, were at first stored in the excavation building in the village. Later they were moved to the Aphrodisias Museum building.